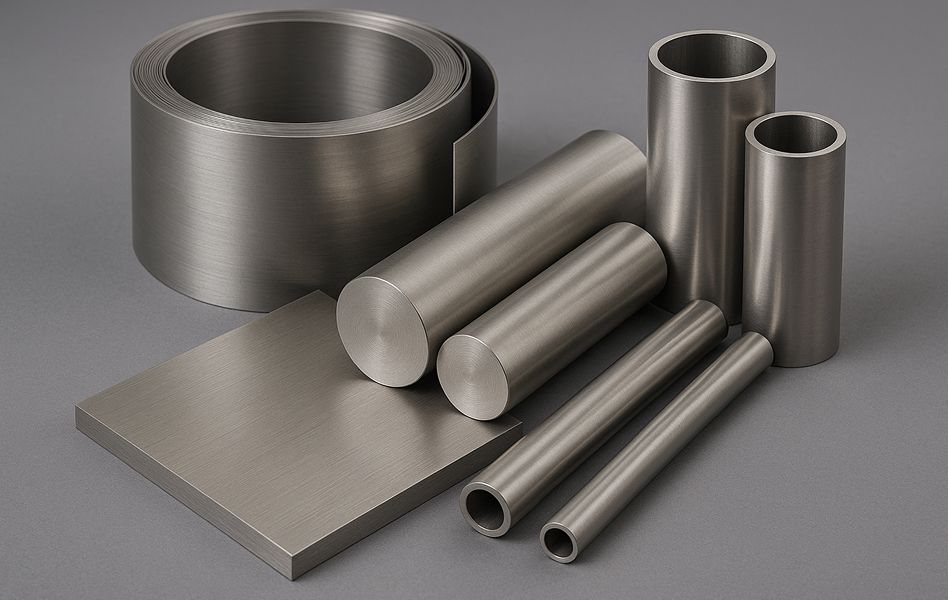
Titanium
It is classified as a general structural metal with a melting point of 1668°C which is higher than iron at 1530°C although its thermal conductivity is relatively low. Titanium shows excellent formability with minimal deformation during fabrication and is located in Group 4 Period 4 of the periodic table with atomic number 22. Among the elements that make up the Earth’s crust including O Si Al Fe Ca Na K and Mg it ranks ninth in abundance. Although titanium is highly reactive it forms a dense and stable oxide film on the surface which provides outstanding corrosion resistance making it suitable for harsh environments. In particular it shows strong resistance to chlorine and is well known for excellent performance in seawater where corrosion conditions are severe.
Applications
| Environmental Industry | Materials for wastewater treatment, water supply systems, and related equipment. |
|---|---|
| Construction | Corrosion-resistant materials for laboratories and chemical plants, and materials for building interiors, exteriors, and food production facilities. |
| Shipbuilding | Materials for ships, marine plants, ship repair, oil production facilities, and submarines. |
| Automotive | Used for vehicle frames, bodies, and exterior components. |
| Structural | General and welded structural materials for bridges, ships, and vehicles. |
| Steel Pipes | Pipes for general, mechanical, heat exchanger, low-temperature, and fluid or gas applications. |
| High-Pressure Gas | Materials for pressure vessels and gas tanks. |
| Special Applications | Materials for automotive parts, chains, blades, and tools. |
Product specifications
Product spec
Thickness : 3~13T
Width : 1,000~2,000W
Length : ~20,000L
Weight Calculation Formula
thickness x width x length x specific gravity x quantity